Solar and Energy storage
The project is made up of a ground-mounted solar photovoltaic (PV) generating station with battery storage, onsite substations and associated infrastructure to generate and export/import electricity in excess of 50MW, as well as areas of landscaping and biodiversity enhancement.
It also includes a grid connection corridor of approximately 10km in length, which will connect the site to the proposed new National Grid Substation near Navenby, using a 400kV underground cable corridor. Fosse Green Energy will then export and import electricity to the national grid.
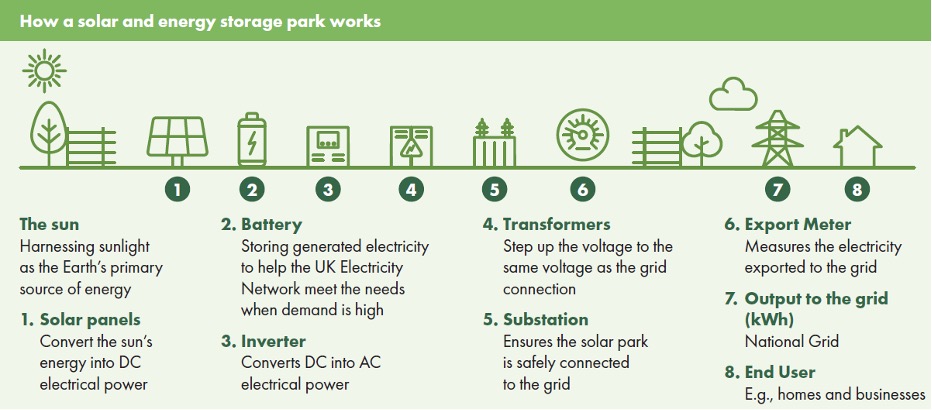
The ground-mounted solar PV panels convert sunlight into DC electrical power. Each panel is likely to have a DC generating capacity of between 400 and 850 watts, or potentially more depending on advances in technology at the time of construction.
Panels are fixed to a mounting structure, otherwise known as tables, which will be arranged in rows.
The solar panel tables will be arranged in either a south facing fixed configuration or a single axis tracker configuration. In a south facing configuration, the tables would be aligned east to west with the panels sloping towards the south, at a fixed angle of 5 to 45 degrees from horizontal.
In a single axis tracker configuration, the panels would move from east to west during the course of the day operated by a small motor. The panels will then reverse this process at the end of each day, returning to a horizontal position where they remain overnight.
What is BESS?
A Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) is proposed for Fosse Green Energy to store the energy produced by the project and release it to the grid when it is most needed. We are considering options for ‘decentralised’ BESS, with battery containers located throughout the Solar PV Array Areas, or ‘centralised’ BESS within a single compound, and would welcome your feedback on these options.